Selected Research Projects *
* click title of projects to unfold the details.
|
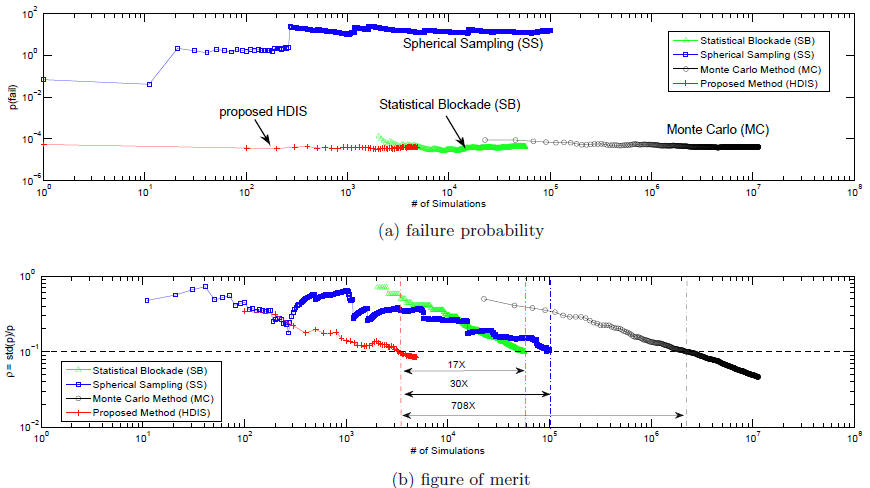
The reliability issue of highly replicated circuits has become increasingly challenging under large-scale process variations, because the circuit failure is a "rare event" with an extremely small probability (e.g., 1e-5~1e-11). Among existing techniques, importance sampling is a very widespread solution providing high efficiency. However, the "curse of high dimensionality" prevents it to be used in high dimensions, therefore, making it unsuitable for real problems in practice. In this work, we proposed a novel and efficient statistical analysis of rare events in high dimension, which has been successfully applied to predict the extremely small failure probability of memory circuits. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first work that applies the importance sampling paradigm to high dimensional problems (e.g., tens or hundreds random variables) . The experiments on an memory circuits (e.g., SRAM bit-cell, delay chain) show the proposed algorithm can provide several orders of magnitude speedup over Monte Carlo method without compromising any accuracy. In addition, the proposed approach is tens times faster than classification based method (e.g., Statistical Blockade) whereas existing importance sampling based methods completely fail to provide reasonable accuracy.
This work is presented in DAC 2012 WIP [O3] and is under review. |
|
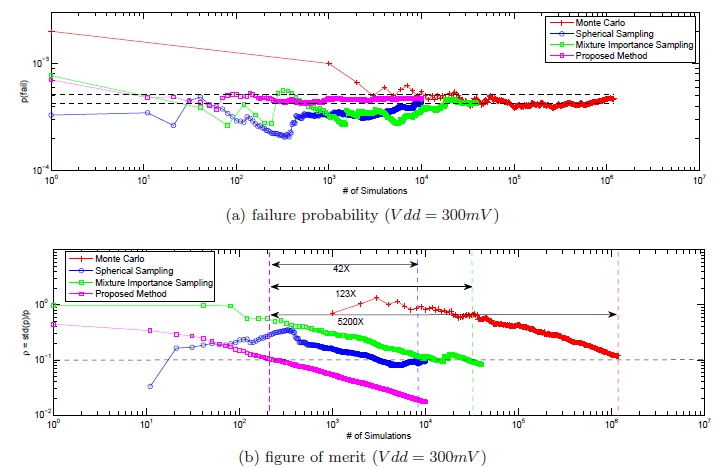
This work tries to estimate the failure probability of rare-failure event in SRAM cell, which is extremely small. We propose to improve the conventional importance sampling method by probability collectives. First, we use the "Kullback-Leibler distance" (KL) to measure the distance between the optimal sampling distributions and the given sampling distributions of variable process parameters. Then, the probability collectives technique is adapted to analytically minimize this KL distance so as to find a sampling distribution as close to the optimal as possible. The proposed algorithm significantly expedite the convergence of importance sampling method. Experiments demonstrate proposed algorithm is 5200X faster than Monte Carlo method and achieves more than 40X speedup over other existing state-of-the-art techniques without compromising any accuracy.
This work has been published by ISPD 2012 [C7]. The source code can be download from here. |
|
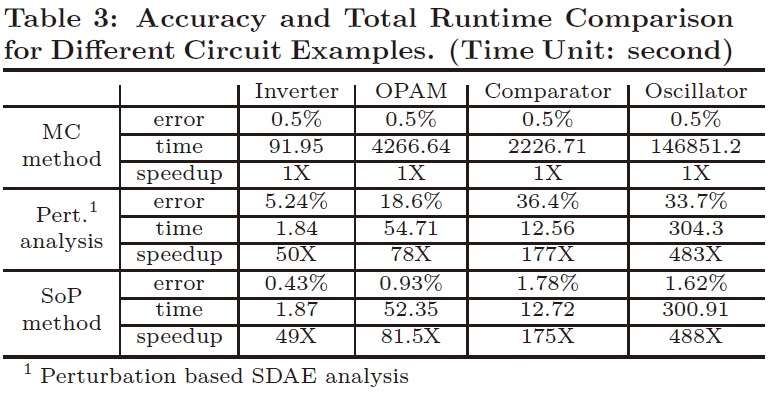
The random device noise has become one of fundamental limits for analog/RF circuits. To describe the effects of device noise in time domain efficiently, this work apply the recent-established polynomial chaos to the stochastic differential algebraic equation (SDAE). As such, the noise variance along the time can be extracted with only one-time calculation. It considers both thermal noise and flicker noise in the transient noise analysis, which can be 488X faster than Monte Carlo method with similar accuracy and achieves on average 6.8X speedup over existing Non-Monte-Carlo approach.
This work has been published by the 48th ACM/IEEE DAC 2011 for publication C[6]. |
|
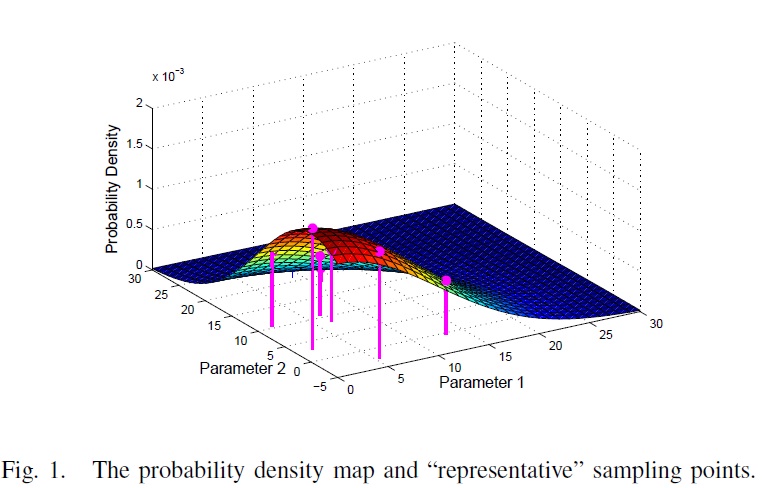
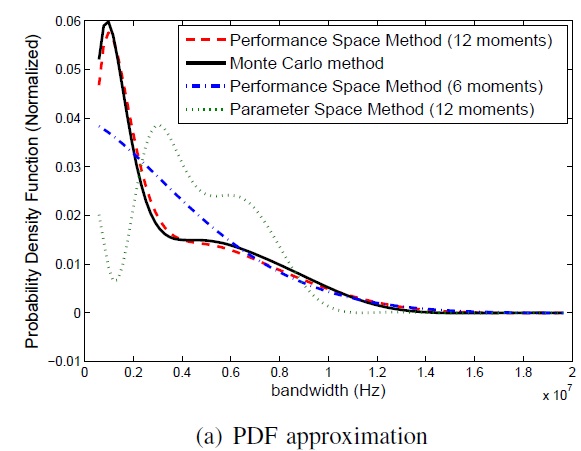
Due to large scale process variations, the performances of analogue circuits (e.g. delay, voltage level, output swing, and etc.) can deviate from their nominal fixed values and have stochastic distributions. It is desired to extract the probability distributions of circuit behavior during the design stage for robust designs. This work leverages the point estimation methods to capture "arbitrary" stochastic variations on circuit behavior efficiently by taking only a few samplings. The proposed algorithm can provide up to 181X speedup over Monte Carlo method with the same accuracy, and 15X speedup over the state-of-the-art approach. The right figure shows the PDF approximation of an operational amplifier with 90 random variable, which needs only 90 samples.
This work was published in ISPD 2011 [C4] and TCAD [J10]. |
|
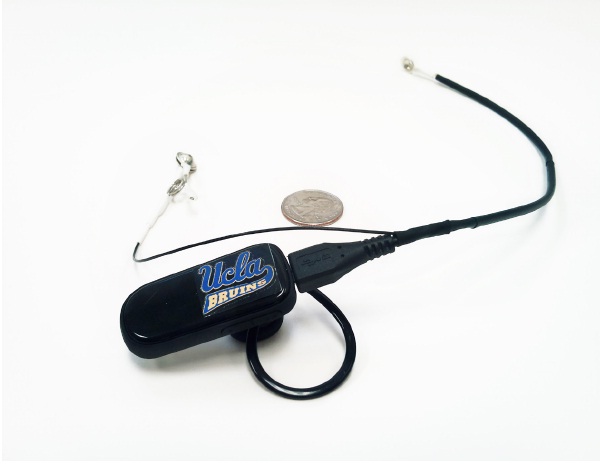
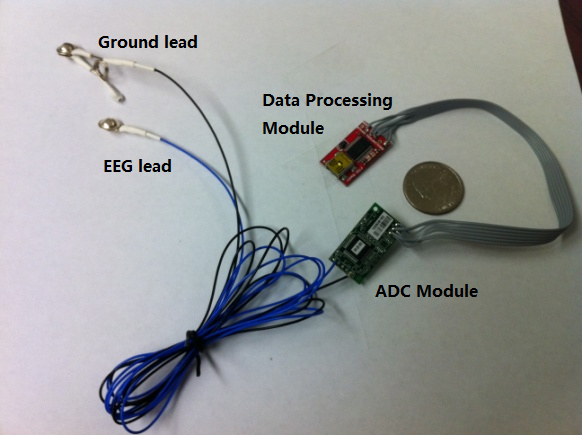
This work builds a low-cost ($19) and wearable (tens grams) BCI system to acquire Electroencephalography (EEG) signals. The system can detect user's concentration based on EEG signal analysis in real-time manner. It can further control the surrounding appliances such as reading lamps, fans and etc. Potential applications include gaming, wheelchair motion control for disabled, and brain health monitoring.
This work has been demoed in the third UCLA Technology and Aging Conference in Oct 2010. Visitors to the conferences, in large numbers, lined-up to try this system, amazed at the BCI's functionality. Also, it has been published in [J6] and reported in BIT and New Media Journal. Collaborators: Wenyao Xu, Ju-Yueh Lee, Prof. Majid Sarrafzadeh |
|
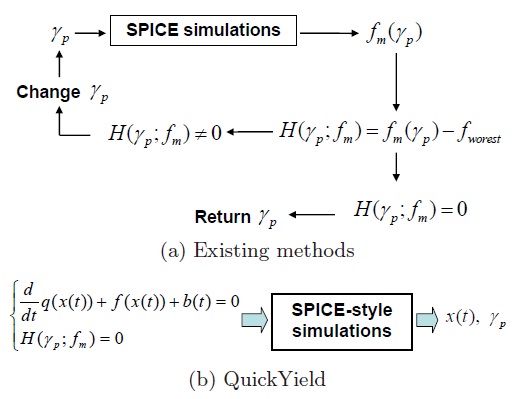
My research proposes a fast algorithm, called "QuickYield", to calculate the parametric yield based on yield boundary separating the success and failure regions. To locate surface points on the yield boundary, the performance constraint is integrated into the differential algebraic equation (DAE) to formulate one augmented nonlinear system, which can be solved with Newton-Raphson iterations for those parameters on the yield boundary. In this way, one-time simulation is needed to locate one surface point. "QuickYield" can achieve 519X speedup over Monte Carlo simulations and 4.7X over the fastest existing approach with the same accuracy.
This work was published in the 47th ACM/IEEE DAC 2010 [C3] and IEEE Design and Test [J8]. |
|
This work explores the efficient extraction of the variational capacitance in presence of process variations. It first defines geometric moments, which relates the potential coefficients with geometry information, and then develops one parallel fast multi-pole algorithm based on those moments. In addition, it presents spectrum pre-conditioner to consider different variation sources incrementally. The entire extraction flow is called "PiCAP", which can achieve 15X speedup over serial counterpart. This work was published in the 46th ACM/IEEE DAC 2009 [C2] and TVLSI [J3]. |
|
This work develops an efficient field solver (named "Mixed Boundary Element Method" or "MBEM" ) to extract the wideband impedance from zero frequency to at least tens of Giga Hertz, which can be applied to complicated 3D structures and obtains great advantage over FastImp (M.I.T developed in 2005), on both accuracy and efficiency. It utilizes the efficient pFFT algorithm (pre-corrected Fast Fourier Transform) to speed up the evaluation of matrix-vector-product (MVP) in iterative solvers such as Generalized Minimal Residual Method (GMRES). Specifically, the complexity of MVP can be reduced from O(N2) to nearly O(N), where N is the number of variables. Moreover, this work presents many numerical optimization skills to avoid redundant operations in order to further improve the efficiency. This work has been published with [J1], and on the 13th ASPDAC’08 [C1] . |
Conference Presentations
- Oral Presentations
- ACM International Symposium on Physical Design 2012, Napa Valley, California, March 26, 2012.
- The Computer-Aided Network Design (CANDE) workshop 2011, San Jose, CA, Nov. 10, 2011.
- UCLA
Electrical
Engineering
Department
Annual Research
Review, Los
Angeles, CA,
Nov. 14, 2011.
Title: "Rare Event Estimation: Capture the infeasible events in uncertainty", [ slides]
slides] - ACM/IEEE 48th Design Automation Conference, San Diego, CA, June5-10, 2011.
- ACM International Symposium on Physical Design, Santa Barbara, California, March 27-30, 2011.
- ACM/IEEE 47th Design Automation Conference, Anaheim, California, June 13 - 18, 2010.
- ACM/IEEE 46th Design Automation Conference, San Francisco, California, July 26 - 31, 2009.
- IEEE 13th Asia South Pacific Design Automation Conference, Seoul, Korea, Jan.21~24, 2008.
- Poster Presentation
- Design Automation Conference Work-In-Progress Session, San Francisco, CA, June4-7, 2012.
- SIGDA Ph.D.
Forum at Design
Automation
Conference, San
Diego, CA,
June5-10, 2011.
Title: "Statistical Modeling and Simulation for VLSI Circuits and Systems", [ slides]
slides] - SRC ICSS
System Contract
Review
Conference, Los
Angeles, CA,
March 7, 2011.
Title: "Stochastic Modeling and Simulation Using Parallel Computing". - UCLA
Electrical
Engineering
Department
Annual Research
Review, Los
Angeles, CA,
March 2, 2011.
Title: "Statistical Modeling and Simulation for VLSI Circuits and Systems". - UCLA
Electrical
Engineering
Department
Annual Research
Review, Los
Angeles, CA, Feb
12, 2010.
Title:"Modeling and Design for Robust Analog Circuits".
Invited Talks
- “Fast Rare Event Estimation in High Dimension with Application to Memory Circuit”, Mentor Graphic, San Jose, CA, Feb. 2012.
- "Stochastic Modeling for VLSI circuit and systems", UCLA, Los Angeles, CA, Feb. 2012.
- “Stochastic Modeling and Validation for Analog/Mixed-Signal Circuits”, Intel Company, San Jose, CA, Feb. 2012.
- "Efficient Parametric Yield Analysis and Optimization", UCLA, Los Angeles, CA, Jan. 2011.
- “Stochastic Simulation for Analog Circuit and Stochastic Yield for Memory”, Tsinghua University, Beijing, China, Dec. 2010.
- "Study on Parametric Yield Analysis for 6-T SRAM Cell", UCLA, Los Angeles, CA, May, 2010.
Professional Services
- Invited reviewer for journals
in the field of VLSI design automation, including
- IEEE Transactions on Computer-Aided-Design of Integrated Circuits and Systems (TCAD)
- IEEE Transactions on Very Large Scale Integration Systems (TVLSI)
- IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems (TCAS)
- IEEE Transactions on Nanotechnology (TNANO)
- ACM Transactions on Design Automation of Electronic Systems (TODAES)
- Invited Reviewer for conferences, including
- IEEE/ACM Design Automation Conference (DAC)
- IEEE/ACM International Conference on Computer-Aided Design (ICCAD)
- IEEE/ACM International Symposium on Circuit and System (ISCAS)
- IEEE/ACM International Symposium on Physical Design (ISPD)
- IEEE/ACM Asia and South Pacific Design Automation Conference (ASP-DAC).
Media Reports
- “Stochastic Behavioral Modeling of Analog/Mixed-Signal Circuits”, EE Times, Brian Bailey (Editor), Feb, 2012.
- “A Brain-Computer Interface to Help the Elderly Reduce the Risk of Falling”, Bruin Innovation & Technology Magazine (BIT), UCLA, Spring 2011.
- “UCLA Students Helping Mobility Impaired to Move the World”, The New Media Journal, Frank Salvato, (Managing Editor), Feb 26, 2011.
Software
- MATLAB solver for rare event
estimation [download]
- includes Monte Carlo and probability collective based Importance Sampling (IS) method (ISPD'12).
- uses 6-T SRAM cell as an example to estimate its read failure probability.
- IS method can provide several orders of magnitude speedup over MC when failure probability is extremely small (e.g., 1e-4~1e-6).
EDA/CAD Selected Conferences
- International Conference on Computer-Aided Design (ICCAD)
- International Conference on Computer Design (ICCD)
- Asia South Pacific Design Automation Conference (ASPDAC)
- TAU Workshop
- Design Automation and Test in Europe (DATE)
- International Symposium on Quality Electronic Design (ISQED)
- International Symposium on Physical Design (ISPD)
- Design Automation Conference (DAC)